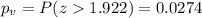Answer:
The statistic for this case would be:
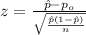
And replacing we got:
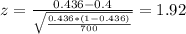
Explanation:
For this case we have the following info:
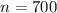 represent the sample size
represent the sample size
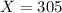 represent the number of employees that earn more than 50000
represent the number of employees that earn more than 50000
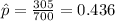
We want to test the following hypothesis:
Nul hyp.
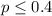
Alternative hyp :
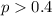
The statistic for this case would be:
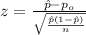
And replacing we got:
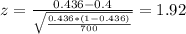
And the p value would be given by: