Answer:
The pressure of the gas is 4.428 atm.
Step-by-step explanation:
Ideal gases are a simplification of real gases that is done to study them more easily. It is considered to be formed by point particles, do not interact with each other and move randomly. It is also considered that the molecules of an ideal gas, in themselves, do not occupy any volume.
Considering a certain amount of ideal gas confined in a container where the pressure, volume and temperature can vary, but keeping the mass constant, that is, without altering the number of moles, the pressure, P, the temperature can be related, T and the volume, V, of an ideal gas using the ideal gas law:
P*V = n*R*T
where R is the ideal gas constant, and n is the number of moles of the gas.
In this case, to know n you must know the molar mass of the CO₂ compound. Being:
then, the molar mass of CO₂ is: 12 g/mole + 2*16 g/mole= 44 g/mole
Then you apply a rule of three: if 44 grams of CO₂ are present in 1 mole, 8.06 grams in how many moles are they?
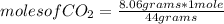
moles of CO₂= 0.18 moles
Then, you know:
- R= 0.082
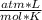
Replacing in the equation of the ideal gas law:
P* 1 L= 0.18 moles* 0.082
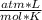 * 300 K
* 300 K
Solving:
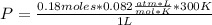
P= 4.428 atm
The pressure of the gas is 4.428 atm.