Answer:
Null and alternative hypothesis:
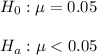
The alternative hypothesis is the one that needs evidence to be supported, while the null hypothesis is the one that can be nullified (reject).
Only if there is enough evidence that thickness is less than 0.05 the null hypothesis will be rejected and the alternative hypothesis claim supported.
A Type I error happens when a true null hypothesis is rejected. In this case we will be purchase a order that is not fulfilling the thickness required.
A Type II error happens when a false null hypothesis is failed to be rejected. In this case, the order has a thickness significantly smaller than 0.05, but the sample gives no enough evidence and the order will not be purchased.
Explanation:
A hypothesis test to see conclusive evidence that the true standard deviation of sheath thickness is less than 0.05 mm will have the following hypothesis:
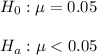
The alternative hypothesis Ha will state that the true mean is significantly smaller than 0.05, while the null hypothesis H0 will state the opposite: that the true mean is not significantly smaller than 0.05.
The alternative hypothesis is the one that needs evidence to be supported, while the null hypothesis is the one that can be nullified (reject).
Only if there is enough evidence that thickness is less than 0.05 the null hypothesis will be rejected and the alternative hypothesis claim supported.