Answer:
a = 4.32*10^15 m/s^2
Step-by-step explanation:
In order to calculate the acceleration of the nitrogen molecule, you take into account that the force experienced by the molecule, is equal to the change in its momentum:
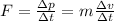 (1)
(1)
m: mass of the nitrogen molecule
Δv: change in the speed of the molecule
Δt: time lapse of the change of the momentum of the molecule = 3.10*10^-13 s
Furthermore, by the Newton second law, you have:
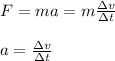 (2)
(2)
The change in the speed is given by:
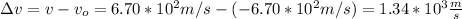
where you have taken into account the direction of the initial and final speed.
You replace the values of all parameters in the equation (1) in order to calculate the acceleration:
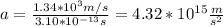
The acceleration of the nitrogen molecule is 4.32*10^15m/s^2