Answer:
1. All real numbers
2. All real numbers except y = 0
3. All real numbers except x = -7
4. All real numbers except b = 10
Explanation:
For any function to be defined at a particular value, it should not be approaching to a value
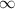 or it should not give us the
or it should not give us the
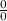 (zero by zero) form when the input is given to the function.
(zero by zero) form when the input is given to the function.
The value of function will depend on the denominator.
Now, let us consider the given functions one by one:
1. 5y+2
Here denominator is 1. So, it can not attain a value
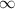 or
or
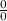 (zero by zero) form
(zero by zero) form
So, for all real numbers, the function is defined.
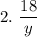
At y = 0, the value
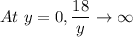
So, the given function is defined for all real numbers except y = 0
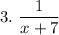
Let us consider denominator:
x + 7 can be zero at a value x = -7
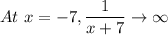
So, the given function is defined for all real numbers except x = -7
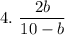
Let us consider denominator:
10-b can be zero at a value b = 10
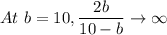
So, the given function is defined for all real numbers except b = 10