Answer:
a) p = 0.5
b) 11.03% probability that more than 55% of them earned more than $837 per week.
c) 99.29% probability that less than 60% of the sample of 150 employees earned more than $837 per week
d) 77.94% probability that between 45% and 55% of the sample of 150 employees earned more than $837 per week
e) 45% is within 2 standard deviations of the mean, which means it would not be unusual if less than 45% of the sample of 150 employees earned more than $755 per week
Explanation:
To solve this question, we need to understand the normal probability distribution and the central limit theorem.
Normal probability distribution
When the distribution is normal, we use the z-score formula.
In a set with mean
 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
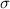 , the zscore of a measure X is given by:
, the zscore of a measure X is given by:
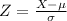
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the pvalue, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
If X is two or more standard deviations from the mean, it is considered unusual.
Central Limit Theorem
The Central Limit Theorem estabilishes that, for a normally distributed random variable X, with mean
 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
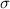 , the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
, the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
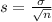 .
.
For a skewed variable, the Central Limit Theorem can also be applied, as long as n is at least 30.
For a proportion p in a sample of size n, the sampling distribution of the sample proportion will be approximately normal with mean
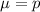 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
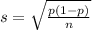
In 2016, the median weekly earnings for people employed full-time in the United States was $837.
This means that 50% of employees earn more than $837 and 50% below.
So we use
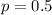
a) What proportion of full-time employees had weekly earnings of more than $837?
From above, p = 0.5
b) A sample of 150 full-time employees is chosen. What is the probability that more than 55% of them earned more than $837 per week?
n = 150, so
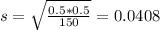
This is 1 subtracted by the pvalue of Z when X = 0.55. So
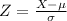
By the Central Limit Theorem
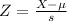
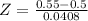
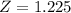
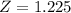 has a pvalue of 0.8897
has a pvalue of 0.8897
1 - 0.8897 = 0.1103
11.03% probability that more than 55% of them earned more than $837 per week.
c) What is the probability that less than 60% of the sample of 150 employees earned more than $837 per week?
This is the pvalue of Z when X = 0.6.
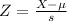
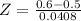
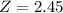
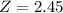 has a pvalue of 0.9929
has a pvalue of 0.9929
99.29% probability that less than 60% of the sample of 150 employees earned more than $837 per week.
d) What is the probability that between 45% and 55% of the sample of 150 employees earned more than $837 per week?
This is the pvalue of Z when X = 0.55 subtracted by the pvalue of Z when X = 0.45.
X = 0.55
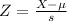
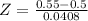
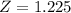
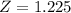 has a pvalue of 0.8897
has a pvalue of 0.8897
X = 0.45
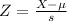
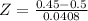
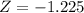
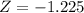 has a pvalue of 0.1103
has a pvalue of 0.1103
0.8897 - 0.1103 = 0.7794
77.94% probability that between 45% and 55% of the sample of 150 employees earned more than $837 per week.
e) Would it be unusual if less than 45% of the sample of 150 employees earned more than $755 per week?
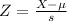
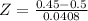
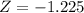
So 45% is within 2 standard deviations of the mean, which means it would not be unusual if less than 45% of the sample of 150 employees earned more than $755 per week