Answer:
The null hypothesis failed to be rejected.
At a significance level of 0.05, there is not enough evidence to support the claim that the mean bad debt ratio for Ohio banks is different than the Midwestern average (3.5%).
Test statistic t = 1.431
Critical values tc = ±2.447
P-value = 0.203
Explanation:
This is a hypothesis t-test for the population mean.
The claim is that the mean bad debt ratio for Ohio banks is different than the Midwestern average (3.5%).
Then, the null and alternative hypothesis are:
H_0: \mu=3.5\\\\H_a:\mu\\eq 3.5
The significance level is 0.05.
The sample has a size n=7.
We calculate the sample mean and standard deviation as:
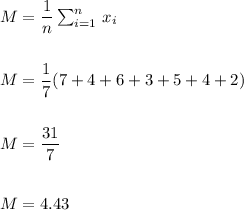
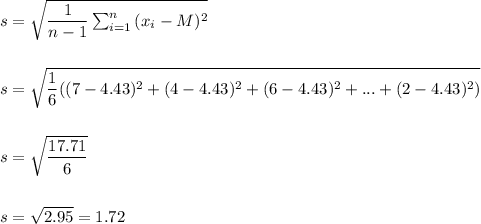
The sample mean is M=4.43.
As the standard deviation of the population is not known, we estimate it with the sample standard deviation, that has a value of s=1.72.
The estimated standard error of the mean is computed using the formula:
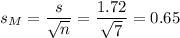
Then, we can calculate the t-statistic as:
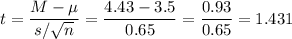
The degrees of freedom for this sample size are:
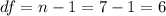
This test is a two-tailed test, with 6 degrees of freedom and t=1.431, so the P-value for this test is calculated as (using a t-table):
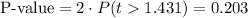
As the P-value (0.203) is bigger than the significance level (0.05), the effect is not significant.
If we use the critical value approach, for this level of confidence, the critical values are tc = ±2.447. The test statistic is within the bounds of the critical values and falls within the acceptance region.
The null hypothesis failed to be rejected.
At a significance level of 0.05, there is not enough evidence to support the claim that the mean bad debt ratio for Ohio banks is different than the Midwestern average (3.5%).