Answer:
677mmHg
Step-by-step explanation:
In answering this question, we use Dalton's law of partial pressures which states that in a mixture of two or more non-reacting gases, the total pressure is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases making up the mixture.
From the question, the gases are oxygen and water vapour.
Therefore the total pressure (
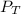 ) is the sum of the partial pressure of oxygen (
) is the sum of the partial pressure of oxygen (
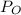 ) and the partial pressure of water vapour (
) and the partial pressure of water vapour (
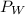 )
)
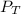 =
=
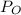 +
+
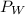 -----------------(i)
-----------------(i)
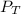 = 692.2mmHg
= 692.2mmHg
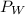 = 14.5mmHg
= 14.5mmHg
Substitute these values into equation (i) as follows;
692.2 =
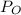 + 14.5
+ 14.5
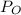 = 692.2 - 14.5
= 692.2 - 14.5
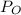 = 677.7
= 677.7
Therefore, the partial pressure of oxygen is 677mmHg