Answer:
The curvature is modelled by
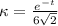 .
.
Explanation:
The equation of the curvature is:
![\kappa = \frac{|\dot {x}\cdot \ddot {y}-\dot{y}\cdot \ddot{x}|}{[\dot{x}^(2)+\dot{y}^(2)]^{(3)/(2) }}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/4oyn2cdvgtmvmz2kzbe6tmpqqsa2mfhhuy.png)
The parametric componentes of the curve are:
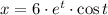 and
and
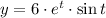
The first and second derivative associated to each component are determined by differentiation rules:
First derivative
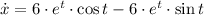 and
and
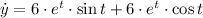
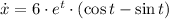 and
and
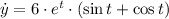
Second derivative
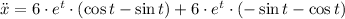
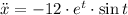
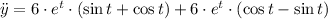
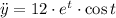
Now, each term is replaced in the the curvature equation:
![\kappa = \frac{\left\{\left[6\cdot e^(t)\cdot (\cos t - \sin t)\right]^(2)+\right[6\cdot e^(t)\cdot (\sin t + \cos t)\left]^(2)\right\}^{(3)/(2)}} }](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/b4wxwggz61ckwxkse6p9alnu37cf1234nf.png)
And the resulting expression is simplified by algebraic and trigonometric means:
![\kappa = \frac{72\cdot e^(2\cdot t)\cdot \cos^(2)t-72\cdot e^(2\cdot t)\cdot \sin t\cdot \cos t + 72\cdot e^(2\cdot t)\cdot \sin^(2)t+72\cdot e^(2\cdot t)\cdot \sin t \cdot \cos t}{[36\cdot e^(2\cdot t)\cdot (\cos^(2)t -2\cdot \cos t \cdot \sin t +\sin^(2)t)+36\cdot e^(2\cdot t)\cdot (\sin^(2)t+2\cdot \cos t \cdot \sin t +\cos^(2) t)]^{(3)/(2) }}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/pb1ly6p4grh8fo2aa9k8wufp5fmld83ga3.png)
![\kappa = \frac{72\cdot e^(2\cdot t)}{[72\cdot e^(2\cdot t)]^{(3)/(2) } }](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/4h4zecrt46reh7auzwek6xwedunmgf01yh.png)
![\kappa = [72\cdot e^(2\cdot t)]^{-(1)/(2) }](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/r5y82k8x6q8zm9q79e0wi8z1dlbs73jur3.png)
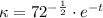
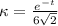
The curvature is modelled by
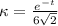 .
.