Answer:
4.76
Step-by-step explanation:
In this case, we have to start with the buffer system:
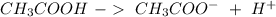
We have an acid (
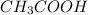 ) and a base (
) and a base (
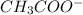 ). Therefore we can write the henderson-hasselbach reaction:
). Therefore we can write the henderson-hasselbach reaction:
![pH~=~pKa+Log([CH_3COO^-])/([CH_3COOH])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/9sby3ccpbclavdjig8drvy7zzq9sk8c1nb.png)
If we want to calculate the pH, we have to calculate the pKa:
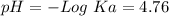
According to the problem, we have the same concentration for the acid and the base 0.1M. Therefore:
![[CH_3COO^-]=[CH_3COOH]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/towvnu7b2xiiaioqfovbevdwzbhbm3ukle.png)
If we divide:
![([CH_3COO^-])/([CH_3COOH])~=~1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/pczcqy5y0zz54q5pmeclbdon9dmv18u9h9.png)
If we do the Log of 1:
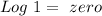
So:
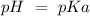
With this in mind, the pH is 4.76.
I hope it helps!