Given Information:
Frequency = f = 60 Hz
Transformer output voltage = Vrms = 6.3 V
Diode voltage drop = Vd = 1 V
Ripper voltage = Vr = 0.25 V
Load resistance = R = 0.5 Ω
Required Information:
a) dc output voltage = V₀ = ?
b) Capacitane = C = ?
Answer:
a) dc output voltage = V₀ = 2.52 V
b) Capacitane = C = 0.336 F
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The average or dc output voltage of a half-wave rectifier is given by
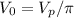
Where Vp is given by
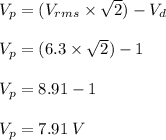
So, the dc output voltage is
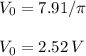
b) The minimum value of C required to maintain the ripple voltage to less than 0.25 V is given by
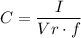
Where I is current, Vr is the ripple voltage and f is the frequency
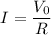
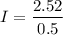
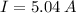
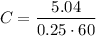
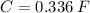
Therefore, 0.336 F is the minimum value of capacitance required to maintain the ripple voltage to less than 0.25 V