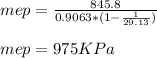Answer:
a) 23.19
b) 2.19
c) 0.597 ( 59.7%)
d) 975 KPa
Step-by-step explanation:
Solution:-
- We will determine the properties of the working fluid (Air) at each state value.
- We will seek help from air standard property tables ( A-22 ) and write down the following:
State 1:
P1 = 95 KPa , T1 = 300 K
u1 = 214.07 KJ/kg , vr1 = 621.2 , Pr1 = 1.386
- Using relations for isentropic compression we determine the reduced pressure value at state 2:
State 2:
P2 = P3 = 7200 KPa
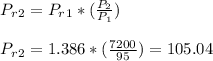
T2 = 979.6 K , vr2 = 26.793 , h2 = 1022.82 KJ/kg
State 3:
P3 = 7200 KPa , T3 = 2150 K
h3 = 2440.3 KJ/kg , vr3 = 2.175 , Pr1 = 1.386
- Using relations for isentropic expansion we determine the reduced volume value at state 4:
State 4:
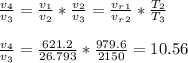
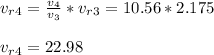
T4 = 1031 K , u4 = 785.75 KJ/kg
a) the compression ratio ( r )
- It is the ratio of volume decreased in the compression stroke ( State 1 -> state 2 ):
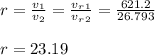
b) the cutoff ratio ( rc )
- It is the ratio of volume increased in the heat-addition process ( State 2 -> state 3 ):
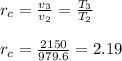
c) the thermal efficiency of the cycle ( nth )
- It is the ratio of total work-output from the cycle and the heat addition (Q23). The net work of the cycle is comprised of both heat addition(St2 - St3) and exhaust (St4 - St1 ). Hence, the work done by the cycle is:
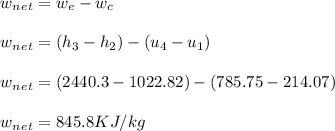
- The thermal efficiency of the cycle would be:
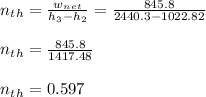
d) the mean effective pressure, mep
- It is the ratio of net work done by the cycle and the displaced volume of the compression stroke ( V1 - V2 ).
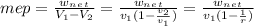
- We need to determine the specific volume of air at state 1. We will use ideal gas equation to determine.
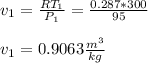
- Now we can use the calculated specific volume ( v1 ), compression ratio ( r ) and the net cycle work ( wnet ) to determine the ( mep ):