Answer:
Explained below.
Explanation:
From the information provided:
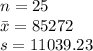
(a)
A hypothesis test is to performed to determine whether the population mean annual administrator salary in Ohio differs from the national mean of $90,000.
The hypothesis is:
H₀: The population mean annual administrator salary in Ohio is same as the national mean of $90,000, i.e. μ = 90000.
Hₐ: The population mean annual administrator salary in Ohio is different from the national mean of $90,000, i.e. μ ≠ 90000.
(b)
As the population standard deviation is not provided, a t-test will be used.
The test statistic value is:
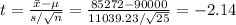
Compute the p-value of the test as follows:
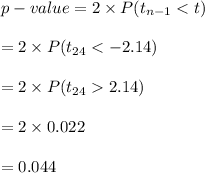
*Use a t-table.
Thus, the p-value of the test is 0.044.
(c)
The significance level of the test is, α = 0.05.
Decision rule:
Reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than the significance level.
p-value = 0.044 < α = 0.05.
The null hypothesis will be rejected at 5% level of significance.
Conclusion:
There is enough evidence to support the claim that the population mean annual administrator salary in Ohio differ from the national mean of $90,000.
(d)
The critical value of t is:
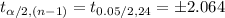
The rejection region can be defined as follows:
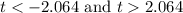
The test statistic value is, t = -2.14.
The test statistic value lies in the rejection region.
Thus, the null hypothesis will be rejected concluding that the population mean annual administrator salary in Ohio differ from the national mean of $90,000.