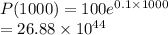Answer:
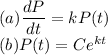
(c)
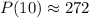
(ii)
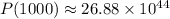
Explanation:
(a)The rate of growth of the population is proportional to the population, this is written as:

(b)

(c)
Suppose the net birthrate of the population is .1, and the initial population is 100.
k=0.1
P(0)=100
Substitution into P(t) gives:
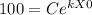
C=100
Therefore:
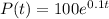
(i)When t=10
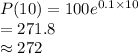
(ii)When t=1000