Answer:
a. The 95% confidence interval for the mean is (33.52, 35.48).
b. The 95% confidence interval for the mean is (34.02, 34.98).
c. n=49 ⇒ Width = 1.95
n=196 ⇒ Width = 0.96
Note: it should be a factor of 2 between the widths, but the different degrees of freedom affects the critical value for each interval, as the sample size is different. It the population standard deviation had been used, the factor would have been exactly 2.
d. 5. Quadrupling the sample size while holding the confidence coefficient fixed decreases the width of the confidence interval by a factor of 2.
Explanation:
a. We have to calculate a 95% confidence interval for the mean.
The population standard deviation is not known, so we have to estimate it from the sample standard deviation and use a t-students distribution to calculate the critical value.
The sample mean is M=34.5.
The sample size is N=49.
When σ is not known, s divided by the square root of N is used as an estimate of σM:
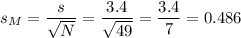
The degrees of freedom for this sample size are:
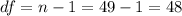
The t-value for a 95% confidence interval and 48 degrees of freedom is t=2.011.
The margin of error (MOE) can be calculated as:
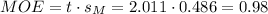
Then, the lower and upper bounds of the confidence interval are:
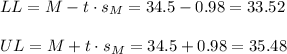
The 95% confidence interval for the mean is (33.52, 35.48).
b. We have to calculate a 95% confidence interval for the mean.
When σ is not known, s divided by the square root of N is used as an estimate of σM:
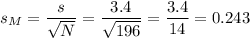
The degrees of freedom for this sample size are:
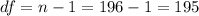
The t-value for a 95% confidence interval and 195 degrees of freedom is t=1.972.
The margin of error (MOE) can be calculated as:
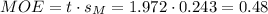
Then, the lower and upper bounds of the confidence interval are:
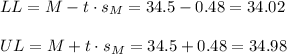
The 95% confidence interval for the mean is (34.02, 34.98).
c. The width of the intervals is:
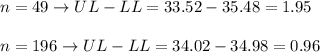
d. The width of the intervals is decreased by a factor of √4=2 when the sample size is quadrupled, while the others factors are fixed.