Answer:
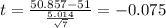
The degrees of freedom are given by:
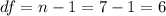
The p value for this case would be given:
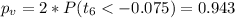
The p value for this case is lower than the significance level so then we have enough evidence to FAIL to reject the null hypothesis and we can conclude that the true mean is not significantly different from 51
Explanation:
Info given
50, 53, 55, 43, 50, 47, 58.
We can calculate the sample mean and deviation with this formula:
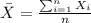
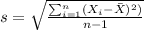
represent the mean height for the sample
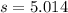 represent the sample standard deviation for the sample
represent the sample standard deviation for the sample
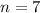 sample size
sample size
represent the value that we want to test
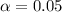 represent the significance level for the hypothesis test.
represent the significance level for the hypothesis test.
t would represent the statistic (variable of interest)
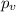 represent the p value
represent the p value
Hypothesis to test
We want to test if the true mean is equal to 51, the system of hypothesis would be:
Null hypothesis:
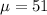
Alternative hypothesis:
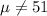
The statistic is given by:
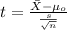 (1)
(1)
Replacing we got:
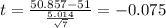
The degrees of freedom are given by:
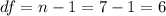
The p value for this case would be given:
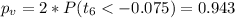
The p value for this case is lower than the significance level so then we have enough evidence to FAIL to reject the null hypothesis and we can conclude that the true mean is not significantly different from 51