Answer:
Δ
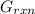 = −51. 4 kJ/mol
= −51. 4 kJ/mol
However, since Δ
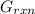 is negative. The hydrolysis of ATP for this reaction is said to be spontaneous
is negative. The hydrolysis of ATP for this reaction is said to be spontaneous
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question; The equation for this reaction can be represented as :
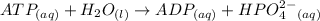
where:
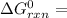 -30.5 kJ/mol
-30.5 kJ/mol
= -30.5 kJ/mol × 1000 J/ 1 kJ
= -30.5 × 10 ⁻³ J/mol
Temperature T = 37 ° C
= (37+273)
= 310 K
pH = 7.0
[ATP] = 5.0 mM
= 5.0mM × 1M/1000mM
= 0.005 M
[ADP] = 0.30 mM
= 0.30 mM × 1M/1000mM
= 0.0003 M
![[HPO_4^(2-)}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/txvzoj4t8vm5wtvfohvkcc07ytiyxhco5x.png) = 5.0 mM
= 5.0 mM
= 5.0mM × 1M/1000mM
= 0.005 M
The objective is to calculate the value for Δ
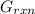 in the biological cell and to determine if the hydrolysis of ATP is spontaneous under these conditions.
in the biological cell and to determine if the hydrolysis of ATP is spontaneous under these conditions.
Now;
From the equation given; the equilibrium constant
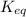 can be expressed as:
can be expressed as:
![K_(eq) = \frac{[ADP][ HPO_4^(2-)]} {[ATP]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/nlsqhcp9hbb8e3swh4ed25rywmsaxdjh0q.png)
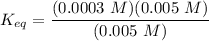
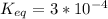
The Δ
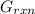 in the biological cell can now be calculated as:
in the biological cell can now be calculated as:
Δ
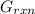 =
=
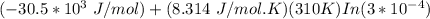
Δ
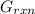 =
=
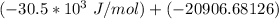
Δ
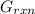 = −51406.68 J/mol
= −51406.68 J/mol
Δ
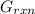 = −51. 4 × 10³ J/mol
= −51. 4 × 10³ J/mol
Δ
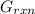 = −51. 4 kJ/mol
= −51. 4 kJ/mol
Thus since Δ
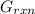 is negative. The hydrolysis for this reaction is said to be spontaneous
is negative. The hydrolysis for this reaction is said to be spontaneous