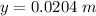Answer:
The capillary rise of the glycerin is most nearly
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The diameter of the glass tube is
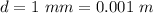
The density of glycerin is
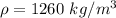
The surface tension of the glycerin is
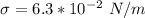
The capillary rise of the glycerin is mathematically represented as
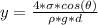
substituting value
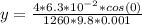
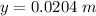
Therefore the height of the glass tube the glycerin was able to cover is