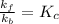Answer: The relationship between the equilibrium constant
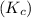 of reaction and the rate constants for the forward
of reaction and the rate constants for the forward
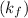 and reverse
and reverse
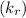 reactions in a single step reaction is
reactions in a single step reaction is
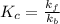
Step-by-step explanation:
Equilibrium constant is the ratio of product of the concentration of products to the product of concentration of reactants.
For example if the reaction is :
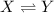
![K_c=([Y])/([X])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/fukmdl9f2s80cdjj4fcwf93uhwcuwjl3zj.png)
Rate of forward direction=
![k_f[X]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/yeedlbaf6vh178f9snp6cpwcrr9v4ta8sq.png)
Rate of backward direction=
![k_b[Y]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/vmo1h9jr3pyoeso3uyp2clzt2v5bwbp2ds.png)
At equilibrium, Rate of forward direction = Rate of backward direction
thus
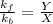
where
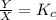
Thus