Answer:
Null hypothesis:
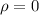
Alternative hypothesis:
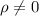
The statistic to check the hypothesis is given by:
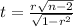
And is distributed with n-2 degreed of freedom. df=n-2
For this case since the calculated values is on the interval (-0.878, 0.878) we can FAIL to reject the null hypothesis and on this case the correlation would be not significant at 5% of significance
Explanation:
In order to test the hypothesis if the correlation coefficient it's significant we have the following hypothesis:
Null hypothesis:
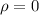
Alternative hypothesis:
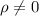
The statistic to check the hypothesis is given by:
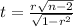
And is distributed with n-2 degreed of freedom. df=n-2
For this case since the calculated values is on the interval (-0.878, 0.878) we can FAIL to reject the null hypothesis and on this case the correlation would be not significant at 5% of significance