Complete question:
The exit nozzle in a jet engine receives air at 1200 K, 150 kPa with negligible kinetic energy. The exit pressure is 80 kPa, and the process is reversible and adiabatic. Use constant specific heat at 300 K to find the exit velocity.
Answer:
The exit velocity is 629.41 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
initial temperature, T₁ = 1200K
initial pressure, P₁ = 150 kPa
final pressure, P₂ = 80 kPa
specific heat at 300 K, Cp = 1004 J/kgK
k = 1.4
Calculate final temperature;
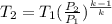
k = 1.4
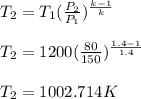
Work done is given as;
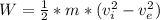
inlet velocity is negligible;
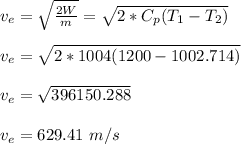
Therefore, the exit velocity is 629.41 m/s