Answer:
The GDP gap is 9 % when there is 4.5 % unemployment.
Explanation:
The statement shows a reverse relationship, where an increase in unemployment is following by decrease in potential GDP and can be translated into the following rate:
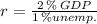
The GDP gap at a given increase in unemployment can be estimated by the following expression:
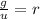
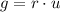
Where:
 - GDP gap-unemployment increase rate, dimensionless.
- GDP gap-unemployment increase rate, dimensionless.
 - Increase in unemployment rate, measured in percentage.
- Increase in unemployment rate, measured in percentage.
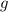 - GDP gap, measured in percentage.
- GDP gap, measured in percentage.
If
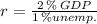 and
and
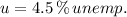 , the GDP gap is:
, the GDP gap is:
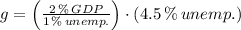
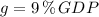
The GDP gap is 9 % when there is 4.5 % unemployment.