Answer:

Contraction
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information;
Above 88° C
zirconium has a BCC crystal structure with a = 0.332 nm
Below this temperature
zirconium has an HCP structure with a = 0.2978 nm and c = 0.4735 nm
the volume of BCC can now be:
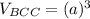
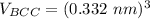
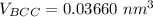
the volume of HCP can now be:
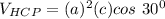
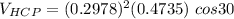
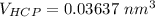
Ths; the volume percent change when BCC zirconium transforms to HCP zirconium can be calculated as:
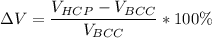
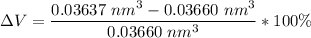

Hence; it is contraction due to what the negative sign portray, The negative sign signifies that there is contraction during cooling