Answer:
The probability that the sample proportion will differ from the population proportion by greater than 0.03 is 0.009.
Explanation:
According to the Central limit theorem, if from an unknown population large samples of sizes n > 30, are selected and the sample proportion for each sample is computed then the sampling distribution of sample proportion follows a Normal distribution.
The mean of this sampling distribution of sample proportion is:
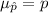
The standard deviation of this sampling distribution of sample proportion is:
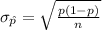
As the sample size is large, i.e. n = 492 > 30, the central limit theorem can be used to approximate the sampling distribution of sample proportion by the normal distribution.
The mean and standard deviation of the sampling distribution of sample proportion are:

Compute the probability that the sample proportion will differ from the population proportion by greater than 0.03 as follows:

![=P(|Z|>2.61)\\\\=1-P(|Z|\leq 2.61)\\\\=1-P(-2.61\leq Z\leq 2.61)\\\\=1-[P(Z\leq 2.61)-P(Z\leq -2.61)]\\\\=1-0.9955+0.0045\\\\=0.0090](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/px8py3iiv9dsr4ieuk0109o5feqeflp8gg.png)
Thus, the probability that the sample proportion will differ from the population proportion by greater than 0.03 is 0.009.