Answer:
a)
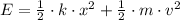 , b) Amplitude of the motion is
, b) Amplitude of the motion is
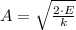 , c) The maximum speed attained by the object during its motion is
, c) The maximum speed attained by the object during its motion is
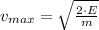 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The total energy of the object is equal to the sum of potential and kinetic energies. That is:
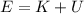
Where:
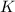 - Kinetic energy, dimensionless.
- Kinetic energy, dimensionless.
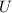 - Potential energy, dimensionless.
- Potential energy, dimensionless.
After replacing each term, the total energy of the object at any point in its motion is:
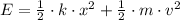
b) The amplitude of the motion occurs when total energy is equal to potential energy, that is, when objects reaches maximum or minimum position with respect to position of equilibrium. That is:
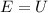
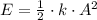
Amplitude is finally cleared:
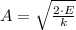
Amplitude of the motion is
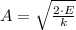 .
.
c) The maximum speed of the motion when total energy is equal to kinetic energy. That is to say:
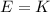
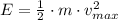
Maximum speed is now cleared:
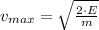
The maximum speed attained by the object during its motion is
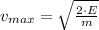 .
.