Answer:
1. Clockwise rotation by π/2 radians
: D
2. Reflection about the x-axis
: E
3. Counterclockwise rotation by π/2 radians
: F
4. The projection onto the x-axis given by T(x,y) = (x,0)
: C
5. Reflection about the y-axis : A
6. Reflection about the line y = x : B
Explanation:
Given a linear transformation
 , one matrix representation of T is obtained by stacking the vectors T(1,0) and T(0,1) in columns.
, one matrix representation of T is obtained by stacking the vectors T(1,0) and T(0,1) in columns.
a) A counter clockwise rotation of
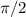 radians sends (1,0) to (0,-1) and it sends (0,1) to (1,0), so the matrix representation is
radians sends (1,0) to (0,-1) and it sends (0,1) to (1,0), so the matrix representation is
![\left[\begin{matrix} 0& 1 \\ -1 & 0 \end{matrix}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/5ong7y85g0oe9lisgye1ptss4bz72sbdoy.png) which corresponds to matrix D.
which corresponds to matrix D.
From now on, I will provide the values of T(1,0) and T(0,1)
b) Reflection about the x-axis T(1,0) = (1,0) and T(0,1) = (0,-1), which corresponds to matrix E.
c) Counterclockwise rotation by π/2 radians T(1,0) = (0,1), T(0,1) = (-1,0). Matrix F
d) The projection onto the x-axis given by T(x,y) = (x,0). T(1,0) = (1,0) T(0,1) = (0,0). Matrix C
e) Reflection about the y-axis T(1,0) = (-1,0) T(0,1) = (0,1). Matrix A
f) Reflection about the line y = x. This transformation corresponds to interchanging the values of x and y. That is, send (x,y) to (y,x). So, in this case
T(1,0) = (0,1) T(0,1) = (1,0). Matrix B