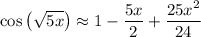Recall the Maclaurin expansion for cos(x), valid for all real x :
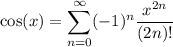
Then replacing x with √5 x (I'm assuming you mean √5 times x, and not √(5x)) gives
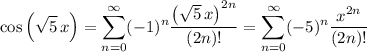
The first 3 terms of the series are
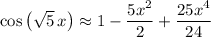
and the general n-th term is as shown in the series.
In case you did mean cos(√(5x)), we would instead end up with
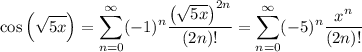
which amounts to replacing the x with √x in the expansion of cos(√5 x) :