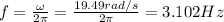Answer:
f = 3.102 Hz
Step-by-step explanation:
In this case you have that the required voltage is the maximum induced emf produced by the rotating generator.
In order to calculate the frequency of rotation of the generator that allows one to obtain 12.0V you use the following formula:
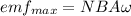 (1)
(1)
N: turns of the armature = 95
B: magnitude of the magnetic field = 0.800T
A: area of the square armature = (9.0cm)^2 = (0.09m)^2 = 8.1*10^-3 m^2
emf_max = 12.0V
w: angular frequency
you solve the equation (1) for w:
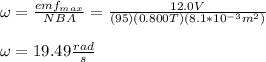
Then, the frequency is: