Answer:
The correct answer is dihydrogen monoxide.
Step-by-step explanation:
In chemistry, there are ionic bonds and molecular/covalent bonds. Because hydrogen and oxygen are both nonmetals, we can confirm that we are dealing with a molecular bond (ionic bonds are normally formed between a metal and a nonmetal).
Now, the naming of molecular compounds is sort of tricky. Instead of changing the endings of the element names like we do with ionic bonds, we add prefixes to the front of the element names in order to signify how many of that element are present in the compound.
Therefore, you will need to firstly find out how many atoms of each element are in the bond.
Water is typically written as
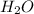 in chemistry (the 2 is a subscript and denotes how many atoms are present of each element in a compound or bond). Therefore, we can confirm that there are two atoms of hydrogen (atomic symbol of H) and one atom of oxygen (atomic symbol of O).
in chemistry (the 2 is a subscript and denotes how many atoms are present of each element in a compound or bond). Therefore, we can confirm that there are two atoms of hydrogen (atomic symbol of H) and one atom of oxygen (atomic symbol of O).
This allows us to expand into prefixes and decide what prefixes you use for each amount of atoms. I have attached a table of these prefixes below for you to use if you need it for reference.
Using the table, we can see that the prefix for two atoms is di-. So, we will place this in front of hydrogen to give us dihydrogen (hydrogen is present twice in the compound or has two atoms present). Then, we always drop the ending of the second element in the compound and change it to -ide. Oxygen works differently than most elements (like Sulfur drops the -ur and becomes sulfide when present in molecular compounds) and drops the -ygen and then becomes named oxide. Finally, we have to add a prefix in front of oxygen (because it is otherwise confusing if we do not and can signify an ionic bond if we are not careful) and this prefix happens to be mono- (one atom of oxygen means that we use the prefix for one atom).
Putting all of this together, we get that
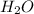 is named dihydrogen monoxide, or more commonly, water.
is named dihydrogen monoxide, or more commonly, water.