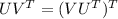Answer:
The inner product holds the commutative property while the outer product does not hold. This indicates that
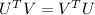 and
and
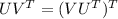
Explanation:
For any two vectors, U and V, given as,
![U=\left[\begin{array}{c}a1\\a2\\a3\\.\\.\\an\end{array}\right] \\V=\left[\begin{array}{c}b1\\b2\\b3\\.\\.\\bn\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/luthvyu4d9pr68lrid3nj63p3n3shb5oxb.png)
Here a1,a2,a3,b1,b2 and b3,.....,an,bn are real numbers
The products are given as
![U^TV=\left[\begin{array}{cccccc}a1&a2&a3&.&.&an\end{array}\right] \left[\begin{array}{c}b1\\b2\\b3\\.\\.\\bn\end{array}\right]\\U^TV=\left[\begin{array}{c}a1*b1+a2*b2+a3*b3+....+an*bn\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/pz8mfobrtd9w04st96egmaxtzfjzvcgdgg.png)
![V^TU=\left[\begin{array}{cccccc}b1&b2&b3&.&.&bn\end{array}\right] \left[\begin{array}{c}a1\\a2\\a3\\.\\.\\an\end{array}\right]\\V^TU=\left[\begin{array}{c}b1*a1+b2*a2+b3*a3+....+bn*an\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/pv4az7vaysyh09gijgyh6g3jyzn3wgiza9.png)
From this, it is clear that the inner product or the scalar product of two vectors U, V is commutative i.e
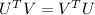
Now for the outer or vector product
![UV^T=\left[\begin{array}{c}a1\\a2\\a3\\.\\.\\an\end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{cccccc}b1&b2&b3&.&.&bn\end{array}\right] \\UV^T=\left[\begin{array}{cccccc}a1*b1&a1*b2&a1*b3&.&.&a1*bn\\a2*b1&a2*b2&a2*b3&.&.&a2*bn\\a3*b1&a3*b2&a3*b3&.&.&a3*bn\\.&.&.&.&.&.\\.&.&.&.&.&.\\an*b1&an*b2&an*b3&.&.&an*bn\end{array}\right]\\UV^T=\left[\begin{array}{cccccc}a1b1&a1b2&a1b3&.&.&a1bn\\a2b1&a2b2&a2b3&.&.&a2bn\\a3b1&a3b2&a3b3&.&.&a3bn\\.&.&.&.&.&.\\.&.&.&.&.&.\\anb1&anb2&anb3&.&.&anbn\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/bgbahrijb4m8b03p0xv0e4eyshndlfgiwl.png)
![VU^T=\left[\begin{array}{c}b1\\b2\\b3\\.\\.\\bn\end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{cccccc}a1&a2&a3&.&.&an\end{array}\right] \\VU^T=\left[\begin{array}{cccccc}b1*a1&b1*a2&b1*a3&.&.&b1*an\\b2*a1&b2*a2&b2*a3&.&.&b2*an\\b3*a1&b3*a2&b3*a3&.&.&b3*an\\.&.&.&.&.&.\\.&.&.&.&.&.\\bn*a1&bn*a2&bn*a3&.&.&bn*an\end{array}\right]\\VU^T=\left[\begin{array}{cccccc}b1a1&b1a2&b1a3&.&.&b1an\\b2a1&b2a2&b2a3&.&.&b2an\\b3a1&b3a2&b3a3&.&.&b3an\\.&.&.&.&.&.\\.&.&.&.&.&.\\bna1&bna2&bna3&.&.&bnan\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/w6syprcn2kweaxzi4ykiss4kz3e0bx19ur.png)
From this, it is clear that the outer product or the vector product of two vectors U, V is not commutative i.e
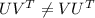
However, it is evident that