Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Calculate ΔG (in kJ) for the following reaction at 1.0 atm for C2H6,
0.5 atm for O2, and
2.0 atm for CO2, and
25 oC:
C2H6 (g) + O2 (g) ---> CO2 (g) + H2O (l) (unbalanced)
ΔGfo C2H6 (g) = - 32.89 kJ/mol;
ΔGfo CO2 (g) = - 394.4 kJ/mol;
ΔGfo H2O (l) = - 237.13 kJ/mol
The balance equation of this reaction is

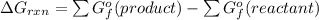
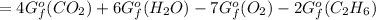
![[4(-394.4)+6(-237.13)-7(0)-2(-32.89)]kJ/mol\\\\=-1577.6-1422.78+65.78\\\\=-3000.38+65.78\\\\=-2934.6kJ/mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/48641tng749b4umv519urdbyrrdwkiii2y.png)