Answer:
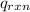 = -13.3 KJ belongs to the bomb calorimeter
= -13.3 KJ belongs to the bomb calorimeter
Step-by-step explanation:
In this question, we are concerned with determining which of the two heats of reaction given, belongs to that in the bomb calorimeter
The kind of calorimetry used in a bomb calorimeter and a coffee-cup calorimeter is different.
In a bomb calorimeter, what we have is a constant volume calorimetry while in a coffee-cup calorimeter, what we have is a constant-pressure calorimetry.
For constant volume calorimetry, the change in volume ΔV = 0 while for constant pressure calorimetry, the change in pressure ΔP = 0.
Mathematically, the relationship between the change in internal energy Δ
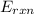 of the reaction, the work of the reaction
of the reaction, the work of the reaction
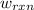 and the heat of the reaction
and the heat of the reaction
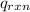 is given by;
is given by;
Δ
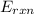 =
=
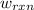 +
+
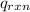
Kindly note that, in a bomb calorimeter, the work of the reaction
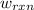 = 0
= 0
Thus, this means that for a bomb calorimeter,
Δ
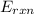 =
=
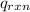
This means that in the bomb calorimeter, the entire internal energy change is converted to heat of the reaction.
In the case of the coffee-cup calorimeter, the work of the reaction is non-zero and it is equal to the product of the pressure and the change in volume.
Thus, mathematically,
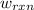 = PΔV
= PΔV
Thus;
Δ
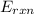 =
=
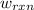 +
+
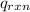 = PΔV +
= PΔV +
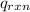
Since for a coffee cup calorimeter, the change in volume is positive(as given in the question), this means that;
ΔV > 0
and PΔV > 0
This automatically means that
Δ
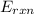 >
>
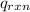
Hence, in the coffee cup calorimeter, the entire change in internal energy is not converted to heat as part is used to do useful work.
Thus, this means that in the coffee cup calorimeter, the value of change in internal energy is greater than the value of heat.
This makes the magnitude of heat in the bomb calorimeter greater than that of the coffee cup calorimeter.
Since -13.3 KJ is the bigger magnitude of the two, then it belongs to the bomb calorimeter