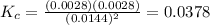Answer: 0.0378
Step-by-step explanation:
To find the equilibrium constant, we will need to fill out the ICE chart.
The I in ICE is initial quantity. In this case, it is the initial concentration. Concentration is in Molarity. The C in ICE is change in each quantity. The E is equilibrium.
2HF(g) ⇄ H₂(g) + F₂(g)
I 0.025 0 0
C -0.0056 +0.0028 +0.0028
E 0.0144 0.0028 0.0028
For the steps below, refer to the ICE chart above.
1. Since we were given the initial of Hf and equilibrium of H₂, we can fill those into the chart.
2. Since we were not given the initial for H₂ or F₂, we will put 0 in their place.
3. For the change, we need to add concentrations to the products to make the reaction reach equilibrium. We would add on the products and subtract from the reactants to equalize the reaction. Since we don't know how much the change in, we can use variable x. We know that the equilibrium of H₂ is 0.0028, we know the change is 0.0028 because 0.0028-0=0.0028. This is also the same for F₂. HF is not 0.0028 because there is 2 of HF so we have to multiply it by 2.
4. With the equilibrium values, we can find the equilibrium constant. It is products over reactants. We use the values of E.
![K_(c) =([H_(2)][F_(2)] )/([HF]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/yozllbyl0pkt1v6gba17hhz94hlmx7vdz0.png)
The [HF]² comes from HF. We more the moles to the exponent when we are calculating the equilibrium constant.