Answer:
Gravitational potential energy to kinetic energy
Step-by-step explanation:
In this case you have a case about conservation of energy.
When the mass is released and allowed to fall, its energy is completely gravitational potential energy with a value of U = mgh. m is the mass, g is the gravitational constant and h is the height to the floor from the mass.
While the mass is falling down part of its potential energy converts to kinetic energy of value K=1/2mv^2, because the mass has been acquiring more and more velocity.
Thus, the kinetic energy is increasing while the potential energy is decreasing.
When the mass is just above the floor (the moment just before the mass hits the floor) all its potential energy has been converted to kinetic energy.
Then, you have that the kinetic energy of the mass when the mass is just above the floor, is equal to the potential energy when the mass is at height of h. That is:
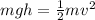
This is how the law of conservation of energy is fulfilled.