Answer: The exit temperature of the gas in deg C is
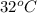 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
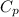 = 1000 J/kg K, R = 500 J/kg K = 0.5 kJ/kg K (as 1 kJ = 1000 J)
= 1000 J/kg K, R = 500 J/kg K = 0.5 kJ/kg K (as 1 kJ = 1000 J)
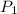 = 100 kPa,
= 100 kPa,
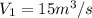
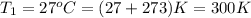
We know that for an ideal gas the mass flow rate will be calculated as follows.
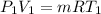
or, m =
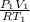
=
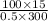
= 10 kg/s
Now, according to the steady flow energy equation:
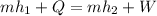
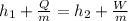
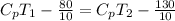
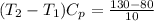
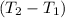 = 5 K
= 5 K
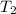 = 5 K + 300 K
= 5 K + 300 K
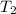 = 305 K
= 305 K
= (305 K - 273 K)
=
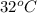
Therefore, we can conclude that the exit temperature of the gas in deg C is
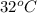 .
.