Answer:
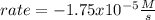
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, for the given information, we can compute the rate of disappearance of NO₂ by using the following rate relationship:
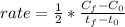
Whereas it is multiplied by the the inverse of the stoichiometric coefficient of NO₂ in the reaction that is 2. Moreover, the subscript f is referred to the final condition and the subscript 0 to the initial condition, thus, we obtain:
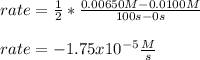
Clearly, it turns out negative since the concentration is diminishing due to its consumption.
Regards.