Answer:
B = 15μT
Step-by-step explanation:
In order to calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field generated by the coaxial cable you use the Ampere's law, which is given by:
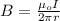 (1)
(1)
μo: magnetic permeability of vacuum = 4π*10^-7 T/A
I: current
r: distance from the wire to the point in which B is calculated
In this case you have two currents with opposite directions, which also generates magnetic opposite magnetic fields. Then, you have (but only for r > radius of the cylindrical conductor) the following equation:
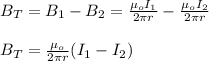 (2)
(2)
I1: current of the central wire = 2.00A
I2: current of the cylindrical conductor = 3.50A
r: distance = 2.00 cm = 0.02 m
You replace the values of all parameters in the equation (2), and you use the absolute value because you need the magnitude of B, not its direction.
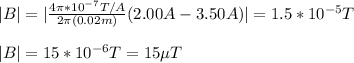
The agnitude of the magnetic field outside the coaxial cable, at a distance of 2.00cm to the center of the cable is 15μT