Answer:
![[PCl_3]_(eq)=0.117M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ngud19v0upl815qcwfg4h1cbfr1h3aqojr.png)
![[Cl_2]_(eq)=0.117M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5wml6dblmdki9eh9pwfxaqmlc6wn760jg2.png)
![[PCl_5]_(eq)=8x10^(-3)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/4w76v7qh76j1nrh54oytsb80xknjcovnfa.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, for the given chemical reaction at equilibrium, we can write the law of mass action as shown below:
![Kc=([PCl_3][Cl_2])/([PCl_5])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/scdr11ft6thomch93zfgmd0ggx5mf5cxx2.png)
That in terms of the ICE methodology is written by means of the change
 due to the reaction extent:
due to the reaction extent:
![Kc=(x*x)/([PCl_5]_0-x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7ce8dk2yh483qvtjnqkn7fd8oi3k6vw1vl.png)
Thus, we need to compute the initial concentration of phosphorous pentachloride:
![[PCl_5]_0=(13.0g*(1mol)/(208.25g) )/(0.500L) =0.125M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5205qwuuz7lbl0wso6x20ygdtstei401bp.png)
So we write:
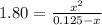
That we solve via either solver or quadratic equation to obtain the solution:
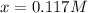
Thereby, the equilibrium concentrations are:
![[PCl_3]_(eq)=x=0.117M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/kf8qp4kd8qazacgms7icb4p4sp548c9vjw.png)
![[Cl_2]_(eq)=x=0.117M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/yuyuq0o1pad8cplm0545flksqygk1bt2h0.png)
![[PCl_5]_(eq)=0.125M-x=0.125M-0.117M=8x10^(-3)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7447beohu0rkfjx13371b6ijrd6g72o6wk.png)
Best regards.