-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Answer:
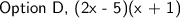
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Given:
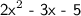
Find:
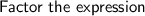
Solution: In order to factor the expression we will have two parenthesis with an x variable and a constant.
Determine important information
- The standard form for a quadratic equation is
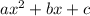 and looking at our equation we can see that a = 2, b = -3, and c = -5.
and looking at our equation we can see that a = 2, b = -3, and c = -5.
- Now we need to determine two numbers that add up to b and multiply up to a * c. So, they must add up to -3 and multiply up to -10. The two numbers that fit the description is -5 and 2.
Determine the factors
We plug in -5x and 2x instead of -3x and factor the expression by grouping.
Therefore, the final answer that fits our solve solution would be option D, (2x - 5)(x + 1).