Answer:
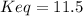
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, for the given reaction at equilibrium:
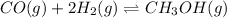
We can write the law of mass action as:
![Keq=([CH_3OH])/([CO][H_2]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ydbahv1zo1k5ck91lsfluspvyos6698nze.png)
That in terms of the change
 due to the reaction extent we can write:
due to the reaction extent we can write:
![Keq=(x)/(([CO]_0-x)([H_2]_0-2x)^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/lliu6lerdu8py9hmt1u5e635kklnc9vfj3.png)
Nevertheless, for the carbon monoxide, we can directly compute
 as shown below:
as shown below:
![[CO]_0=(0.45mol)/(1.00L)=0.45M\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hsxh1jtxhw7tkr3ivo2wqobeo2tegcrzie.png)
![[H_2]_0=(0.57mol)/(1.00L)=0.57M\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/zghcm1vqfw4qbim9dgtvsprddywcg5rptm.png)
![[CO]_(eq)=(0.28mol)/(1.00L)=0.28M\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/p23ls7khp8ahpx6tfj6vxsvl9gdt17p4yb.png)
![x=[CO]_0-[CO]_(eq)=0.45M-0.28M=0.17M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/bq0o4j2szsr8eoy6ndrjbm1vbm8qzqay8x.png)
Finally, we can compute the equilibrium constant:
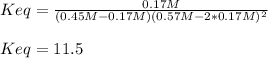
Best regards.