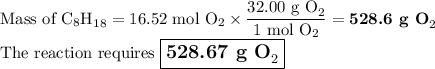Answer:
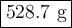
Step-by-step explanation:
It often helps to write the heat as if it were a reactant or a product in the thermochemical equation.
Then you can consider it to be 11018 "moles" of "kJ"
We will need a chemical equation with masses and molar masses, so, let's gather all the information in one place.
M_r: 32.00
2C₈H₁₈ + 25O₂ ⟶ 16CO₂ + 8H₂O + 11 018 kJ
n/mol: 7280
1. Moles of O₂
The molar ratio is 25 mol O₂:11 018 kJ
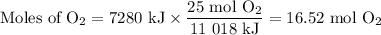
2. Mass of O₂