Answer:
Explanation:
An option to buy a stock is priced at $150. If the stock closes above 30 next Thursday, the option will be worth $1000. If it closes below 20, the option will be worth nothing, and if it closes between 20 and 30, the option will be worth $200. A trader thinks there is a 50% chance that the stock will close in the 20-30 range, a 20% chance that it will close above 30, and a 30% chance that it will fall below 20.
a) Let X represent the price of the option
x P(X=x)
$1000 20/100 = 0.2
$200 50/100 = 0.5
$0 30/100 = 0.3
b) Expected option price
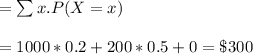
Therefore expected gain = $300 - $150 = $150
c) The trader should buy the stock. Since there is an positive expected gain($150) in trading that stock option.