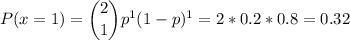Answer:
The probability that at exactly one of them does exactly two language classes is 0.32.
Explanation:
We can model this variable as a binomial random variable with sample size n=2.
The probability of success, meaning the probability that a student is in exactly two language classes can be calculated as the division between the number of students that are taking exactly two classes and the total number of students.
The number of students that are taking exactly two classes is equal to the sum of the number of students that are taking two classes, minus the number of students that are taking the three classes:
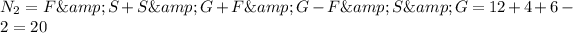
Then, the probabilty of success p is:
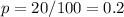
The probability that k students are in exactly two classes can be calcualted as:
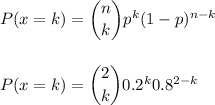
Then, the probability that at exactly one of them does exactly two language classes is: