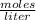Answer:
The molar concentration of the final solution is 1.71
Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity is a way of expressing the concentration of solutions and indicates the number of moles of solute dissolved per liter of solution.
The molarity of a solution is calculated by dividing the moles of the solute by the volume of the solution.:
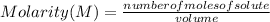
Molarity is expressed in units (
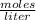 ).
).
Then, the number of moles of solute can be calculated as:
number of moles of solute= molarity* volume
So, in this case, the final concentration can be calculated as:
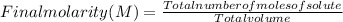
where, being 65 mL=0.065 L, 125 mL=0.125 L and 190 mL=0.190 L (because 1000 mL= 1 L):
- Total number of moles of solute= 0.065 L*0.513
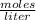 + 0.125 L*2.33
+ 0.125 L*2.33
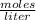 = 0.033345 moles + 0.29125 moles= 0.324595 moles
= 0.033345 moles + 0.29125 moles= 0.324595 moles - Total volume= 65 mL + 125 mL= 190 mL= 0.190 L
Replacing:
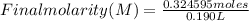
Final molarity ≅ 1.71
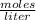
The molar concentration of the final solution is 1.71