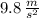Answer:
acceleration = 9.8 m/s^2
Explanation:
The problem expects the user to do the rate of change between any two pairs of (time, velocity) from the table, and see that they all render the same value. Notice as well that the rate of change of a difference in velocities divided a difference in time, will render units of acceleration (in this case
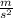
Let's use for example (0 s ,0 m/s) and the following point: (1 s, 9.8 m/s)
the rate of change is:
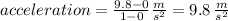
In fact you can use any two pairs of the table, and will get the same result.
So this is the acceleration is