Answer:
Explanation:
The objective is to compute that more runs are scored in games for which DH is used
Let
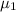 denote the population mean number of runs scored for DH group
denote the population mean number of runs scored for DH group
Let
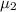 denote the population mean number of runs scored for DH group
denote the population mean number of runs scored for DH group
Let
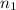 and
and
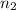 denote the sample sizes for DH and no DH
denote the sample sizes for DH and no DH
From the available information
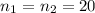
The population standard deviation of runs score is 2.54 for both the groups.
That is
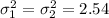
The null hypothesis is
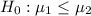
The alternative hypothesis is
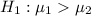
Let the level of significance
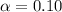
Since, the population standard deviation for both the group is known , even though the sample size is less than 30 , use z test
The test statistic is
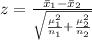
The sample mean for the DH group is computed as
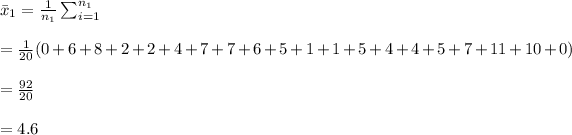
The sample mean of no DH is computed as
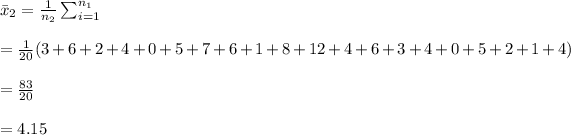
The test statistic is
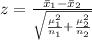

P-Value
From the alternative hypothesis, it is clear that the test is one tailed test
P-value = P(Z > z)
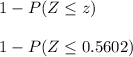
1 - normsdist (0.5602)
(using excel function "normsdist(z)")
= 1 - 0.7123
= 0.2877
Therefore, the P-Value is 0.2877
Decision Rule
Reject the null hypothesis , if the p-value is less than the level of significance . that is p-value is < 0.10
Here, the p-value is 0.2877 which is greater than the level of significance 0.10
so , fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is no sufficient evidence to support the claim that more runs scored in games for which DH is used.