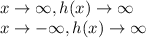Answer:
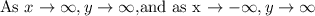
Explanation:
Given the polynomial function:
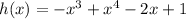
To examine its end behavior, we create a table of values that we can then examine.

From the table, we see a repeating pattern of positive values of h(x) with h(1)=-1 being an axis of symmetry.
Therefore, as: