Answer:
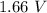
Step-by-step explanation:
We have to start with the half-reactions for both ions:
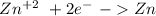 V= -0.76
V= -0.76
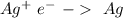 V= +0.80
V= +0.80
If we want a spontaneous reaction (galvanic cell) we have to flip the first reaction, so:
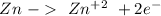 V= +0.76
V= +0.76
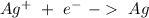 V= +0.80
V= +0.80
If we want to calculate ºE we have to add the two values, so:
ºE=0.76+0.80 = 1.56 V
Now, we have different concentrations. So, if we want to calculate E we have to use the nerts equation:
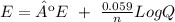
On this case, Q is equal to:
![Q=([Zn^+^2])/([Ag^+]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/4vl2g453ou0x0nar78paecqibd9x5q401r.png)
Because the total reaction is:
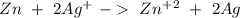
So, the value of "Q" is:
![Q=([0.052 M])/([0.0042]^2)=2947.84](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/a23u39s0iu87c1myst4gtzb7ktoexm1fvf.png)
Now, we can plug all the values in the equation (n=2, because the amount of electrons transferred is 2). So:
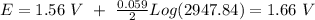
I hope it helps!