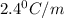Answer: The molal boiling point elevation constant
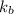 of X is
of X is
Step-by-step explanation:
Formula used for Elevation in boiling point :
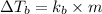
or,
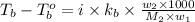
where,
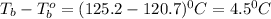
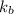 = boiling point constant = ?
= boiling point constant = ?
m = molality
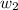 = mass of solute (urea) = 55.4 g
= mass of solute (urea) = 55.4 g
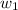 = mass of solvent X = 500 g
= mass of solvent X = 500 g
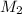 = molar mass of solute (urea) = 60 g/mol
= molar mass of solute (urea) = 60 g/mol
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
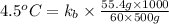
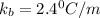
Thus the molal boiling point elevation constant
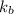 of X is
of X is