Answer:
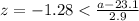
And if we solve for a we got
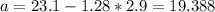
And for the 90 percentile we can do this:
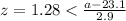
And if we solve for a we got
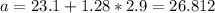
The P10 would be 19.388 and the P90 26.812
Explanation:
Let X the random variable that represent the chocolate chip cookies of a population, and for this case we know the distribution for X is given by:
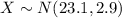
Where
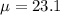 and
and
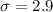
For this part we want to find a value a, such that we satisfy this condition:
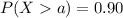 (a)
(a)
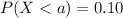 (b)
(b)
We can find a z score value who that satisfy the condition with 0.10 of the area on the left and 0.90 of the area on the right it's z=-1.28.
Using this value we can do this:
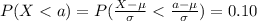
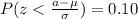
And we can solve for the value of interest
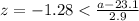
And if we solve for a we got
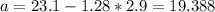
And for the 90 percentile we can do this:
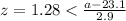
And if we solve for a we got
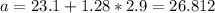
The P10 would be 19.388 and the P90 26.812